niponica is a web magazine that introduces modern Japan to people all over the world.
2015 No.15

To read the e-book you need to have JavaScript enabled in your browser and a free Flash Player plug-in from Adobe Systems Inc. installed.
Japan, Land of Water

A Marriage of Technology and Water
Japan is rich in water resources, as the people well appreciate. And now, developers have come up with new H2O ideas to save resources while improving lifestyles at the same time.
Photos: Toto Ltd., Panasonic Corporation, Toshiba Lifestyle Products & Services Corporation, Fukuoka City Waterworks Bureau, Poly-Glu Social Business Co., Ltd., Hashimoto Laboratory of the University of Tokyo, and Dream Creativity Ltd.
Water conservation technology, developed in Japan
Japan is located in a part of the world where precipitation is generally high, but often the country also experiences dry spells and other forms of weather-related adversity. In response, household appliance manufacturers and cities are finding new ways to conserve water.
Showerheads:
Mixing air with water
Conventional water-conserving showerheads emit less water, so the smaller flow generally comes out under greater pressure, hitting the skin hard enough to cause discomfort. The solution? A product developed by Toto Ltd., which mixes air with the water. It reduces water use by more than 35% while providing a wash that is both effective and pleasant.

Toilets:
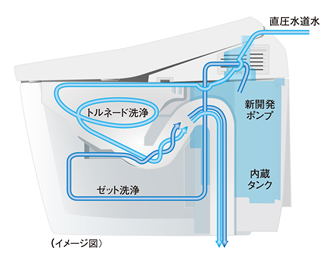
The world’s most efficient flush
Toilet manufacturers keep searching for an even better way to get an effective flush with less water. The Tornado Wash-flush system uses a whirlpool to force everything to the center of the bowl, and then the Jet Wash system takes over, combining two types of flow to clean thoroughly. Some models have lowered water consumption to 3.8 liters per flush, better than any other toilet in the world.
Washing machines:
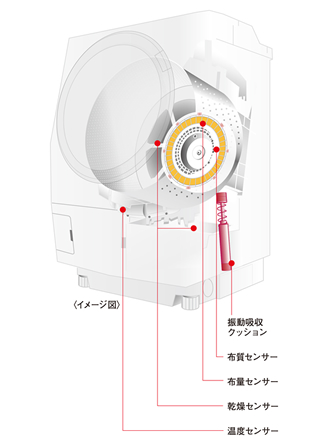
They decide how much to use
Today it is standard for washing machines to use water sparingly. Toshiba’s latest drum type models go further, with sensors that detect the temperature, the amount of laundry to be washed, and the type of fabric. Then the machine decides the optimum amount of water to use during the wash and rinse cycles. A vibration absorption damper prevents the load from becoming unbalanced during the spin cycle, ensuring a good wash while saving even more water.
Dishwashers:
A complete wash with less water
People tend to assume that when it comes to washing, machines use more water than hands. But some machines have turned that on its head. A good example is the dishwasher: at the kitchen sink, many people keep the tap on while washing and rinsing, going through about 84 liters of H2O for dishes used by a family of six. Some new dishwashers use less water to begin with, and their efficient recycle function slashes consumption even more, for both the wash and rinse cycles. Panasonic’s latest models leave dishes sparkling clean after using just 11 liters for that same family of six.
Cities:
Fukuoka residents band together to conserve
In 1978 a dry spell forced the city of Fukuoka to limit its water supply for a long 287 days. From that experience sprang the desire to transform Fukuoka into a model water conservation city, and citizens and the local government have worked as one to achieve this goal. The municipal Water Management Center monitors the amount of water being used 24 hours a day, to ensure efficiency in its supply everywhere in the city. Fukuoka also maintains a scheduled program of leakage prevention, including leak checks and pipe replacements. If each resident were to cut their daily water use by 10 liters, after one year the water saved would be equivalent to the amount in an average reservoir behind a dam. With facts like these in mind, city residents are waging a “Citizens’ Reservoir” campaign to create yet another “source” of nature’s water.