Web Japan > Trends in Japan > Tech & Life > Making Life Comfortable with Sunlight
Making Life Comfortable with Sunlight

Sunlight is indispensable to us. In Japan, new technology that uses sunlight is making life more comfortable.
The 21st century has been lauded as “the era of the environment” as the world faces a host of problems such as global warming, as well as air and water pollution. As a consequence, there is a growing interest in Japan for new technologies that make use of sunlight. In addition to solar power, which is an important source of renewable energy, new applications that utilize sunlight have been developed to clean the air and water.
Photocatalyst that Cleans Like Magic
There is a special type of material that works in tandem with sunlight to change its surroundings, almost like magic. This unique material was discovered in Japan, and is known as a photocatalyst. As it has been commercialized mainly in Japan, it is considered to be an original Japanese technology, and Japan remains the driving force for the global development of photocatalyst technology.
Titanium dioxide (TiO2) is a typical photocatalyst, with remarkable photocatalytic decomposition and superhydrophilicity properties. The photocatalytic decomposition feature of TiO2 is powerful, and it facilitates the decomposition of almost all organic substances into carbon dioxide (CO2) and water. Therefore, the photocatalyst is useful for deodorization, sterilization, and antifouling purposes. The superhydrophilicity of TiO2 can be demonstrated via the elimination of harmful substances using just sunlight and water. Interestingly, when walls coated with a photocatalyst are wetted, dirt on the external surface will wash off naturally.
Owing to their distinct functionalities, photocatalysts are widely used in housing construction materials, electrical appliances, roads, clothing, and other miscellaneous consumables.
Cleaning with Light

Photocatalyst decomposition accelerated test. This is a photo of a test that uses water colored ink instead of dirt. When ultraviolet light strikes it, active oxygen is generated and the ink water color is removed. (Photo courtesy of TOTO LTD.)
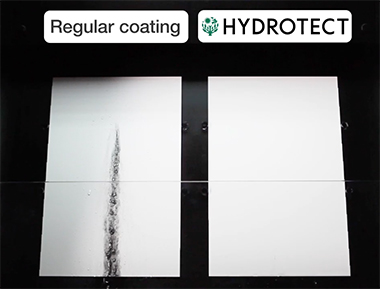
A test to remove dirt with water. The plate on the left had ordinary coating applied, and the one on the right had a photocatalyst coating applied and came clean using only water. (Photo courtesy of TOTO LTD.)
Hydrotect, the functional coating that was developed to leverage the decomposition power and hydrophilicity of TiO2, also cleans the air while using the power of sunlight and rain for self-cleaning.
Aided by sunlight, dirt and dust build-up can be controlled, and oil stains caused by automobile and factory emissions, along with smoke, are first decomposed and then washed off by rain. In addition, Hydrotect is an environmentally friendly coating as it converts substances that pollute the atmosphere into harmless components, and improves the atmospheric air quality by removing these pollutants. It is widely used as an exterior coating that keeps standard house walls clean for an extended duration, and by companies that are focused on environmental protection and by countries with atmospheric pollution issues.
This air-cleaning function of the photocatalyst is also exploited in family-type air cleaners. As conventional air cleaners mainly use filters for physical filtration, their performance drops when the filters get dirty. However, as this technology decomposes harmful substances with a photocatalyst upon entering the air cleaners, filtered materials are less likely to accumulate. In principle, photocatalyst-assisted air cleaners will have a long-lasting effective cleaning performance.
Getting Warmer with Sunlight
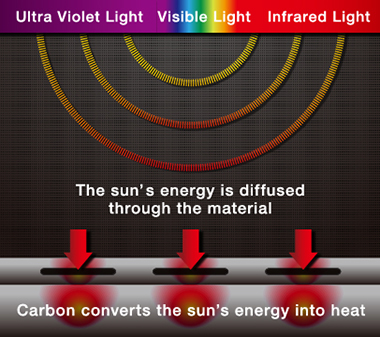
HEATNAVI® material creates warmth by absorbing almost all wavelengths of sunlight. (Photo courtesy of DESCENTE LTD.)

Because this jacket that uses the heat-retentive material HEATNAVI® is also designed to be lightweight, it meets the needs of athletes looking for ease of movement and warmth. (Photo courtesy of DESCENTE LTD.)
Novel technology that uses sunlight is also being incorporated into clothing materials. A material developed by a Japanese sportswear maker aims to provide better heat management functionality with the help of sunlight. In addition to visible light, sunlight is made up of several other wavelengths, including ultraviolet and infrared radiation that cannot be seen by the naked eyes. This synthetic material absorbs all of the sunlight's wavelengths to create heat.
Sunlight reaches the earth not only when the sky is clear but also during cloudy days. Even though the amount of heat exchange is small, this material is able to efficiently convert sunlight into heat and is thus capable of warming the wearer in any weather. As the material warms the wearer in the outdoors, it will also work during warm-up sessions before sports. Presently, the material is used for various sportswear including golf, trekking, ski and soccer apparels to keep athletes warm in cold weather.
In Japan, cutting-edge technology that uses sunlight is making our life more comfortable.
